Rspack 0.4 and Rsbuild 0.1 Release Announcement
Announcing Rsbuild v0.1

We are pleased to announce the release of Rsbuild v0.1!
Rsbuild is an Rspack-based build tool, designed to be an enhanced Rspack CLI that is both more user friendly and out-of-the-box. Rsbuild is the ideal solution for those looking to migrate from Webpack to Rspack. It significantly reduces configuration by 90% while offering a 10x build speed.
🚀 Performance
The build performance of Rsbuild is on par with native Rspack. Considering that Rsbuild includes more out-of-the-box features, its performance will be slightly lower than Rspack.
This is the time it takes to build 1000 React components:

The data is based on the benchmark built by the Farm team, more info in performance-compare.
🔥 Features
Rsbuild has the following features:
-
Easy to Configure: One of the goals of Rsbuild is to provide out-of-the-box build capabilities for Rspack users, allowing developers to start a web project with zero configuration. In addition, Rsbuild provides semantic build configuration to reduce the learning curve for Rspack configuration.
-
Performance Oriented: Rsbuild integrates high-performance Rust-based tools from the community, including Rspack and SWC, to deliver top-notch build speed and development experience. Compared to webpack-based tools like Create React App and Vue CLI, Rsbuild provides 5 to 10 times faster build performance and lighter dependencies.
-
Plugin Ecosystem: Rsbuild has a lightweight plugin system and includes a range of high-quality official plugins. Furthermore, Rsbuild is compatible with most webpack plugins and all Rspack plugins, allowing users to leverage existing community or in-house plugins in Rsbuild without the need for rewriting code.
-
Stable Artifacts: Rsbuild is designed with a strong focus on the stability of build artifacts. It ensures high consistency between artifacts in the development environment and production builds, and automatically completes syntax downgrading and polyfill injection. Rsbuild also provides plugins for type checking and artifact syntax validation to prevent quality and compatibility issues in production code.
-
Framework Agnostic: Rsbuild is not coupled with any front-end UI framework. It supports frameworks like React, Vue 3, Vue 2, Svelte, Solid and Lit through plugins, and plans to support more UI frameworks from the community in the future.
💡 Next Step
Currently, Rsbuild is still evolving rapidly and plans to introduce many more powerful new features.
For example, we are developing Rsbuild Doctor, a robust build analysis tool that can be used with all Rspack and Webpack projects. It will provide a visual user interface to help developers analyze build times, duplicate dependencies, code transformation processes, and more, making it easier to locate and resolve build issues.
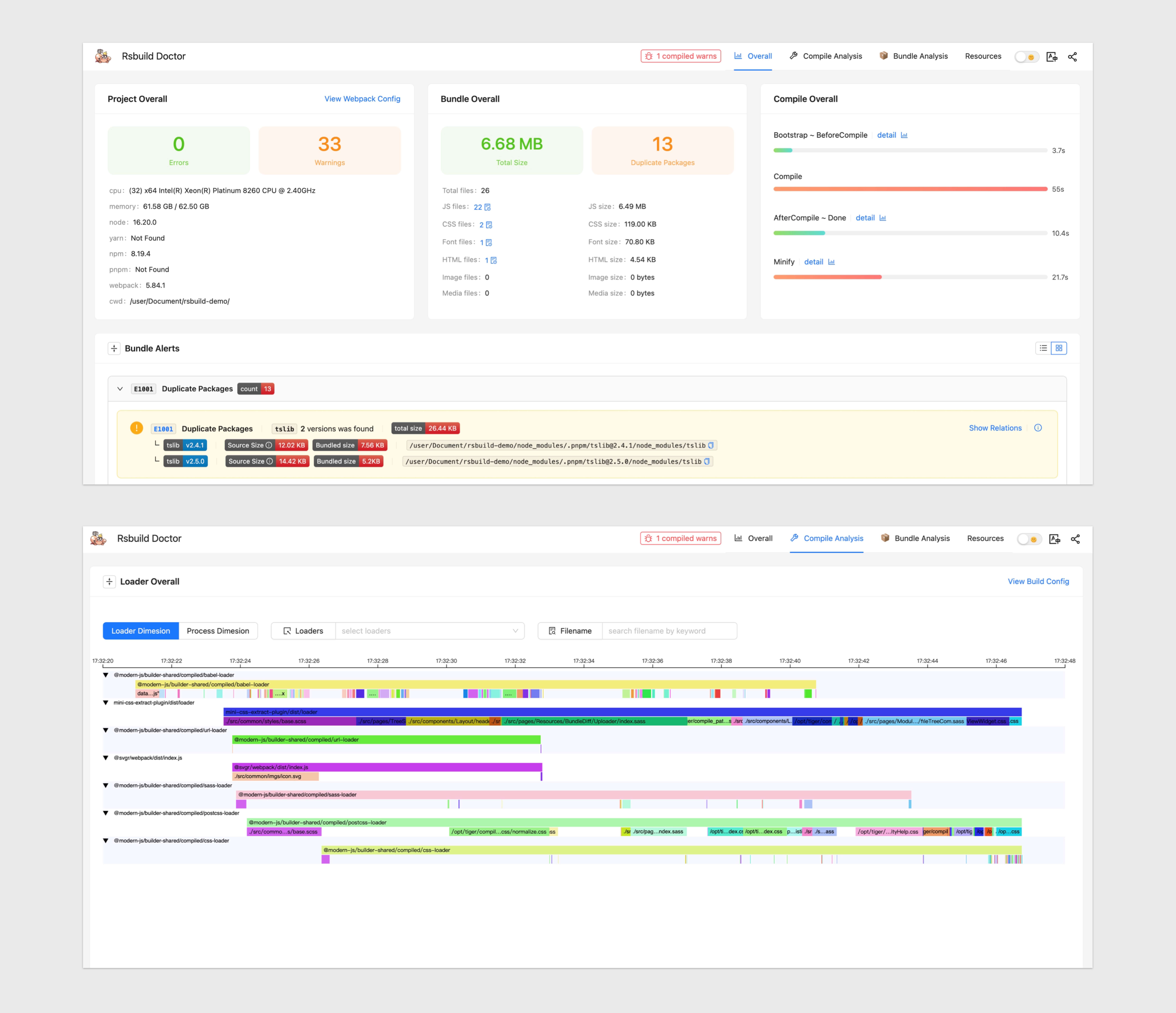
We will be releasing the first working version of Rsbuild Doctor soon. Thereafter, Rsbuild will iterate in sync with Rspack, with plans to release version 1.0 in the first half of 2024.
Feel free to check out the Rsbuild repository to learn more 🙌.
Rspack 0.4 Major Changes
Drop NodeJS 14 Support
Rspack no longer supports Node.js 14, Node.js 16+ is now required.
Make @rspack/core as peer dependency of @rspack/cli
@rspack/core is now a peer dependency of @rspack/cli rather than a direct dependency. This means that you need to manually install @rspack/core with @rspack/cli now. aligning Rspack more closely with webpack. In the long term, the positioning of @rspack/cli will no longer be an out-of-the-box solution. We will align @rspack/cli with webpack-cli and may even directly support the use of @rspack/core in webpack-cli. We recommend Rsbuild as an out-of-the-box solution.
Deprecating default transformation
experiments.rspackFuture.disableTransformByDefault is enabled by default in v0.4.0. For people that still need the legacy behavior, you may manually set this option to false.
This feature primarily addresses three categories of problems: builtins code transformation features, target, and custom Rule.type.
- Removal of support for some builtins features:
- builtins.relay: moved to
rspackExperiments.relay - builtins.react: moved to
jsc.transform.react - builtins.emotion: moved to
rspackExperiments.emotion - builtins.pluginImport: moved to
rspackExperiments.import - builtins.decorator: moved to
jsc.parser.decorator - builtins.presetEnv: moved to
jsc.env
- target will not downgrade user-side code(including
node_modules)
- Removed non-webpack compatible Rule.type
These types have been removed:
"typescript""jsx""tsx"
For JS-related types, only the following will be retained:
"javascript/auto""javascript/esm""javascript/dynamic"
Refer to this for the complete migration guide.
Check out our previous discussion here.
Deprecating builtin.react.refresh
With experiments.rspackFuture.disableTransformByDefault is enabled by default in v0.4.0, builtin.react.refresh has also been deprecated. Now we recommend using @rspack/plugin-react-refresh to enable react fast refresh.
Checkout here for more details.
Deprecating builtin:sass-loader
builtin:sass-loader has now been deprecated. If you are using it, migrate to sass-loader. Rspack will remove builtin:sass-loader in v0.5.0.
Deprecating experiments.incrementalRebuild
experiments.incrementalRebuild has now been deprecated. Rspack will remove it in v0.5.0.
Refactoring export api in @rspack/core
Before, some APIs should not be exported accidentally exported through re-export from @rspack/core. Now with this refactor, we clean up the export APIs from @rspack/core.
This shouldn't break anything, but if you are using unintentionally exported APIs, this may break you, and you may be using Rspack in the hacky way.
If there is a real need for removed APIs from this refactor, please raise an issue in the Rspack repository.
Deprecatingbuiltins.devFriendlySplitChunks andexperiments.newSplitChunks
In order to full migrate to Webpack's split chunks implementation, these fields are deprecated. Rspack will remove these fields in v0.5.0.
Enable newResolver by default
oxc_resolver is now enabled by default.
oxc_resolver is a module resolver written in Rust provided by the oxc project. The new resolver has passed all of enhanced-resolve's test suite. It is 5 times faster than previous implementation, and 28 times faster than enhanced-resolve.
The new resolver can be configured to read tsconfig.json's compilerOptions.paths and references field and provides better support for nested path alias. See API resolve.tsConfig for details.
To opt out of the new resolver, set experiments.rspackFuture.newResolver to false.
Migration Guide
There is a migrate example demonstrating how to migrate from Rspack 0.3.14 to Rspack 0.4.0.
Choose@rspack/cli orRsbuild?
If your application is a CSR application, we strongly encourage you to use Rsbuild instead of configuring Rspack yourself, as Rsbuild is much easier to use compared to @rspack/cli.
Upgrade Node.js Version
Rspack no longer supports Node.js 14 as of version 0.4.0; Node.js 16+ is now required.
Install@rspack/core Manually with@rspack/cli
Usebuiltin:swc-loader to Support Module Transformation
Rspack no longer transforms files by default as of version 0.4.0, you can still enable old transform behavior by the following setting
But we suggest you use builtin:swc-loader to transform files now. More details are available in Deprecating Default Transformation.
Use@rspack/plugin-react-refresh for React Applications
builtin.react.refresh does not work when we disable the default transformation, so you need to use @rspack/plugin-react-refresh to enable fast refresh. More details are available in Deprecating builtin.react.refresh.
Migrating builtin options to builtin plugins
In v0.4.0, Rspack deprecated some of the builtin options and migrated them to internal plugins.
Currently, Rspack's internal plugins are divided into two categories:
- Plugins compatible with Webpack, such as DefinePlugin, ProvidePlugin, etc. This part has been fully aligned with webpack.
- Rspack-specific plugins, such as SwcJsMinimizerRspackPlugin, CopyRspackPlugin, etc.
The original builtins.define can be migrated as follows:
For builtins.html, it can be directly migrated to HtmlRspackPlugin:
When there are multiple configurations in builtins.html, multiple plugin instances can be created:
For builtins.copy, it can be directly migrated to CopyRspackPlugin.
For the original builtins.minifyOptions, we provide SwcJsMinimizerRspackPlugin:
Other builtin options can be directly referred to the rspack internal plugins for migration, or completed according to the CLI prompts after upgrading to v0.4.0.
